Arduino Satellite

ArduSat, short for “Arduino Satellite”, is an educational nanosatellite built in the CubeSat form factor that carries a suite of sensors and a payload computer that can be reprogrammed while in space. The user-programmable payload computer is comprised of an array of Arduino processors (AVR processors), and can run code developed on the ubiquitous, open-source Arduino software development platform. ArduSats were invented with the purpose of creating an inexpensive, accessible development platform in space on which students, teachers, hobbyists, and researchers could affordably create and run their own custom-built experiments and applications.
Users can design their own space-based applications, experiments, and even space-games using the ubiquitous Arduino open-source prototyping platform. Once the application has passed ground testing on an ArduSat clone, users can upload their applications to the satellite’s payload computer in space, where it is watchdogged and maintained by the satellite’s main computer. From there, the applications are free to sample data from the payload sensors and bus, take pictures, and return data to the user’s web browser whenever the satellite is in range of a participating ground station. At the end of the user’s experiment period, which can be up to a week in length, any remaining data is downlinked and returned to the user. We have also developed free training videos that help users develop their space applications and are continually pushing open-source code out to the community to help coming up with the most inventive uses of space.
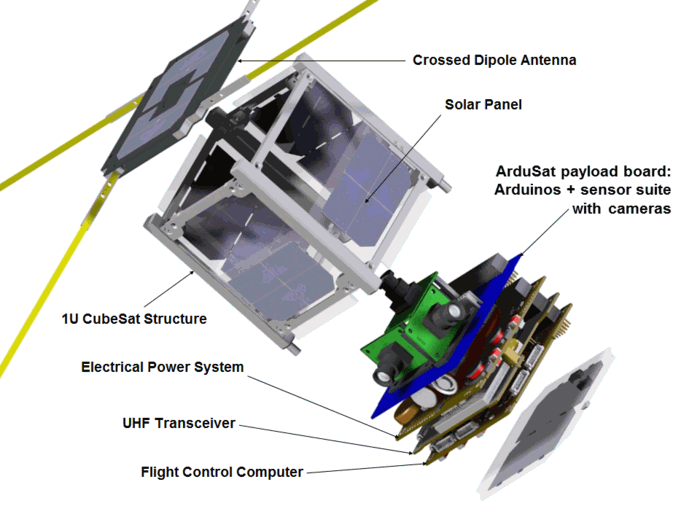
The satellite’s payload consists a suite of sensors, including an optical spectrometer, Geiger counter, atmospheric sensor, infrared sensor, accelerometer & gyro, magnetometer, sun sensor, electromagnetic wave sensor, dual-frequency GPS receiver (for ionospheric studies), a megapixel camera, and more. The sensors (and other telemetry values) are sampled by the user-generated programs running on the payload computer. ArduSat fits in the 1U CubeSat form factor, with a total mass of only 1.3kg and outer envelope of 10cm x 10cm x 10cm (excluding the deployable dipole antenna). The development of the first ArduSat, a 1U CubeSat with a prototype of the Arduino-based payload computer, began in April 2012 as a volunteer effort by four graduate students at the International Space University. In June 2012, the founders formed the ArduSat Inc, a not-for-profit corporation whose purpose is to make the ArduSat space development platform accessible and affordable to students. The ArduSat project was featured on the crowd-funding website Kickstarter where, in addition to raising substantial awareness and attracting nearly 700 private space enthusiasts as direct contributors, it raised enough support to fund the development of two 1U ArduSat satellites.

ArduSat-1
ArduSat is a miniature cubic satellite, measuring 10 cm along each edge and weighing about 1 kg. Onboard it will have a suite of 25+ sensors, including three cameras, a Geiger counter, spectrometer, magnetometer. The 1U cubesat was deployed from ISS on the 19 Nov 2013, 12:18 UTC.
NASA-Catalog: 39412
Beacon
437.000 MHz, CW
Downlink
437.325 MHz, 9k6 MSK, CCSDS encoding
Call
WG9XFC-1
Status
inactive
Orbital Parameter
NORAD 39412 COSPAR designator 1998-067-DA Inclination 51.649 RA of A. Node 229.610 Eccentricity 0.0006629 Argument of Perigee 174.450 Revs per day 15.56174936 Period 1h 32m 32s (92.53 min) Semi-major axis 6 777 km Perigee x Apogee 394 x 403 km BStar (drag term) 0.000857330 1/ER Mean anomaly 258.957
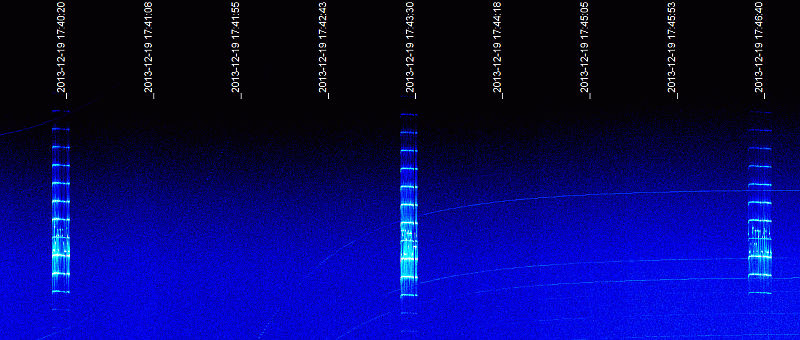
CW Telemetrie
Battery voltage (uint16_t), RX_counter (number of received valid data packets, uint32_t), TX_counter (number of sent valid data packets, uint32_t), “WG9XFC-1" 18 Dec 2013 ----------- 07:36:10 UTC WG9XFC-1 E0 07:39:20 UTC WG9XFC-1 A6.74 07:42:30 UTC WG9XFC-1 D0
ArduSat-X
ArduSat-X is a miniature cubic satellite, measuring 10 cm along each edge and weighing about 1 kg. Onboard it will have a suite of 25+ sensors, including three cameras, a Geiger counter, spectrometer, magnetometer. The 1U cubesat was deployed from ISS on the 19 Nov 2013, 12:18 UTC.
NASA-Catalog: 39414
Beacon
437.005 MHz, CW
Downlink
437.345 MHz, 9k6 MSK, CCSDS encoding
Call
WG9XFC-X
Status
CW beacon active
Orbital Parameter
NORAD 39414 COSPAR designator 1998-067-DC Inclination 51.650 RA of A. Node 229.602 Eccentricity 0.0007008 Argument of Perigee 173.487 Revs per day 15.56248332 Period 1h 32m 31s (92.52 min) Semi-major axis 6 777 km Perigee x Apogee 394 x 403 km BStar (drag term) 0.000861150 1/ER Mean anomaly 259.435
CW Telemetrie
Battery voltage (uint16_t), RX_counter (number of received valid data packets, uint32_t), TX_counter (number of sent valid data packets, uint32_t), “WG9XFC-X” 28 Dec 2013 ------------------------ 11:15 UTC wg9xfc-x e4791 12:44 UTC wg9xfc-x a8.34 12:47 UTC wg9xfc-x d2871 12:51 UTC wg9xfc-x e4791 14:23 UTC wg9xfc-x d2871 14:26 UTC wg9xfc-x e4791 14:30 UTC wg9xfc-x a8.33

ArduSat-2
ArduSat is a miniature cubic satellite, measuring 10 cm along each edge and weighing about 1 kg. Onboard it will have a suite of 25+ sensors, including three cameras, a Geiger counter, spectrometer, magnetometer. The 1U cubesat was deployed from ISS on the 19 Nov 2013, 12:18 UTC.
NASA-Catalog: tbd
Beacon
437.000 MHz, CW
Downlink
437.x MHz, 9k6 MSK, CCSDS encoding
Call
WG9XFC-2
Status
deployment from ISS (KIBO) on Feb 6
Links und weitere Informationen
Submitting a beacon packet
You can submit a beacon as plain text to nanosatisfi@gmail.com – be sure to put the word “packet” in the subject line so that we can parse it quickly.